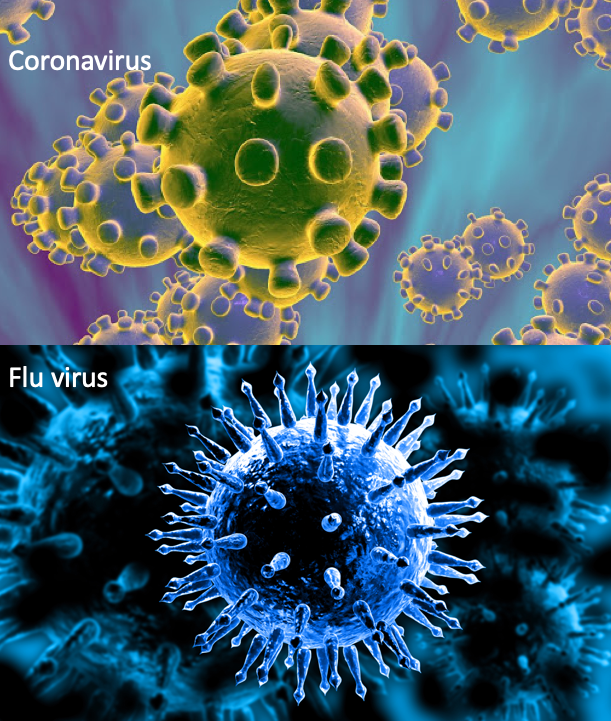
The new coronavirus outbreak has made headlines in recent weeks, but there’s another viral epidemic hitting countries around the world: flu season. But how do these viruses compare, and which one is really more worrisome?
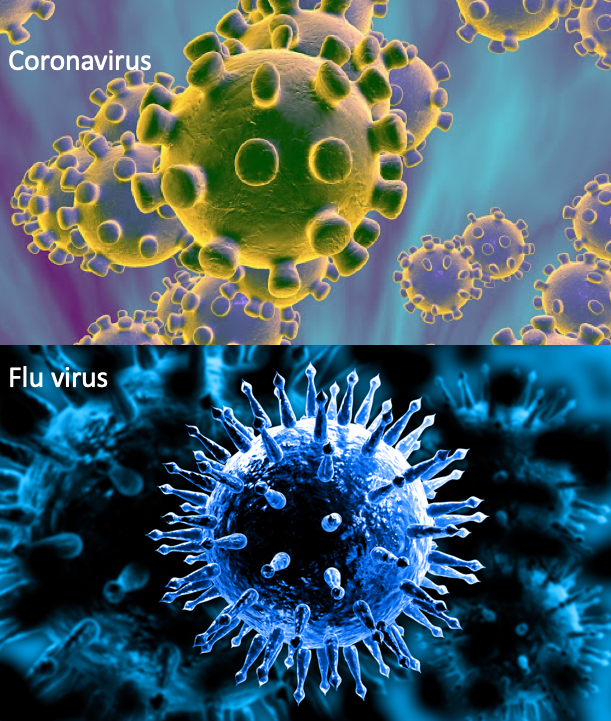
So far, the new coronavirus, dubbed COVID-19, has led to more than 75,000 illnesses and 2,000 deaths, primarily in mainland China. But that’s nothing compared with the flu, also called influenza. In the U.S. alone, the flu has already caused an estimated 26 million illnesses, 250,000 hospitalizations and 14,000 deaths this season, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
That said, scientists have studied seasonal flu for decades. So, despite the danger of it, we know a lot about flu viruses and what to expect each season. In contrast, very little is known about COVID-19 because it’s so new. This means COVID-19 is something of a wild card in terms of how far it will spread and how many deaths it will cause.
Scientists are racing to find out more about COVID-19, and our understanding of the virus that causes it and the threat it poses may change as new information becomes available. Based on what is known so far, here’s how it compares with the flu.
Symptoms And Severity
Both seasonal flu viruses (which include influenza A and influenza B viruses) and COVID-19 are contagious viruses that cause respiratory illness.
Typical flu symptoms include fever, cough, sore throat, muscle aches, headaches, runny or stuffy nose, fatigue and, sometimes, vomiting and diarrhea, according to the CDC. Flu symptoms often come on suddenly. Most people who get the flu will recover in less than two weeks. But in some people, the flu causes complications, including pneumonia. So far this flu season, about 1% of people in the United States have developed symptoms severe enough to be hospitalized, which is similar to the rate last season, according to data from the CDC.
With COVID-19, doctors are still trying to understand the full picture of disease symptoms and severity. In a small study of about 100 people with the virus, published Jan. 30 in the journal, The Lancet, the most common symptoms were fever, cough and shortness of breath. Only about 5% of patients in that study reported sore throat and runny nose, and only 1-2% reported diarrhea, nausea and vomiting.
In a more recent study, considered the largest on COVID-19 cases to date, researchers from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Protection, analyzed 44,672 confirmed cases in China between Dec. 31, 09 and Feb. 11, 2020. Of those cases, 80.9% (or 36,160 cases) were considered mild, 13.8% (6,168 cases) severe and 4.7% (2,087) critical. “Critical cases were those that exhibited respiratory failure, septic shock, and/or multiple organ dysfunction/failure,” the researchers wrote in the paper published in China CDC Weekly.
It’s important to note that, because respiratory viruses cause similar symptoms, it can be difficult to distinguish different respiratory viruses based on symptoms alone, according to WHO.
Virus Transmission
The measure scientists use to determine how easily a virus spreads is known as the “basic reproduction number,” or R0 (pronounced R-nought). This is an estimate of the average number of people who catch the virus from a single infected person, Live science previously reported. The flu has an R0 value of about 1.3, according to The New York Times.
Researchers are still working to determine the R0 for COVID-19. A study published Jan. 29 in the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) estimated an R0 value for the new coronavirus to be 2.2, meaning each infected person has been spreading the virus to an average of 2.2 people.
It’s important to note that R0 is not necessarily a constant number. Estimates can vary by location, depending on such factors as how often people come into contact with each other and the efforts taken to reduce viral spread, Live Science previously reported.
Source: Live Science